Artificial Intelligence is an innovation through which changes have never been witnessed in many industries and many efficiencies. However, this quick pace of adoption has also converted into a big reason to worry about. Herein, artificial intelligence security comes as one major concern. This blog shares information about the security threats that have to be kept in mind while adopting AI, the potential risks, and the strategies to mitigate them.
Introduction of AI Security
The AI systems that support advancements in such fields as health, finance, autonomous vehicles, and even Cybersecurity are core. The deeper AI becomes the functionality or capability of these systems, the more significant it is to realize the security consequences that come with their integration.
Check Out Security Challenges Faced in AI
Data Privacy and Integrity:
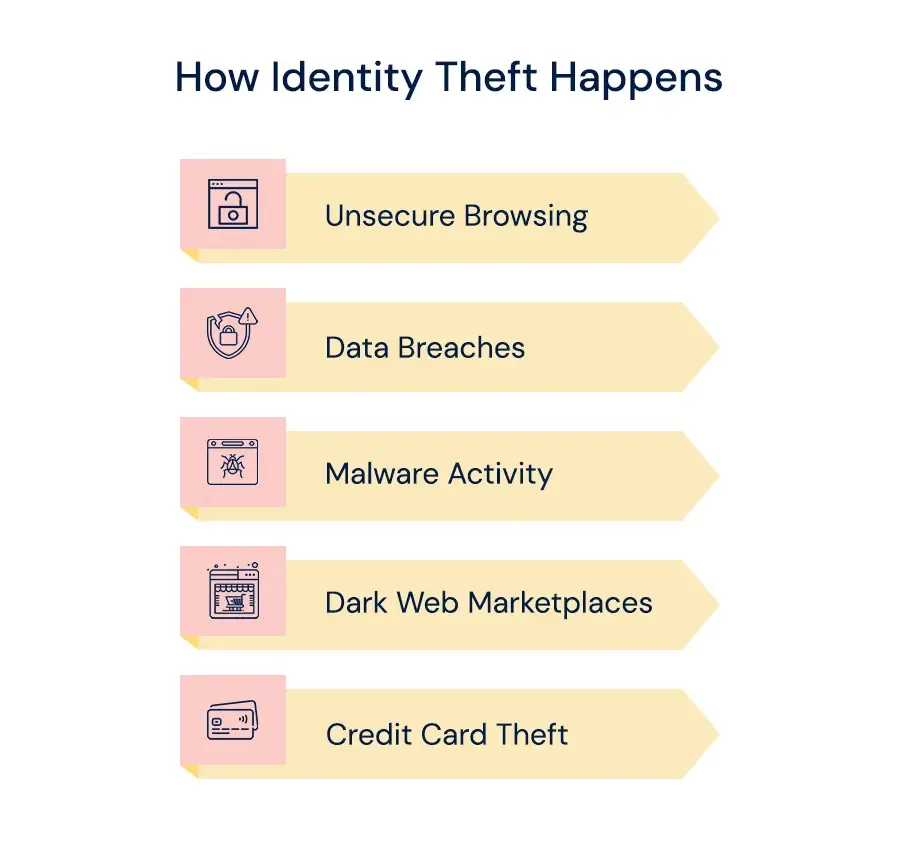
Artificial intelligence systems process and train a lot of data, so careful consideration of the dangers posed by cybercriminals is required. This is the type of data that most often consists of personal information. As a result, she may be exposed to enemy attacks. Ensuring data integrity and protecting privacy will be of great importance in the future in terms of preventing access attempts and potential data breaches.
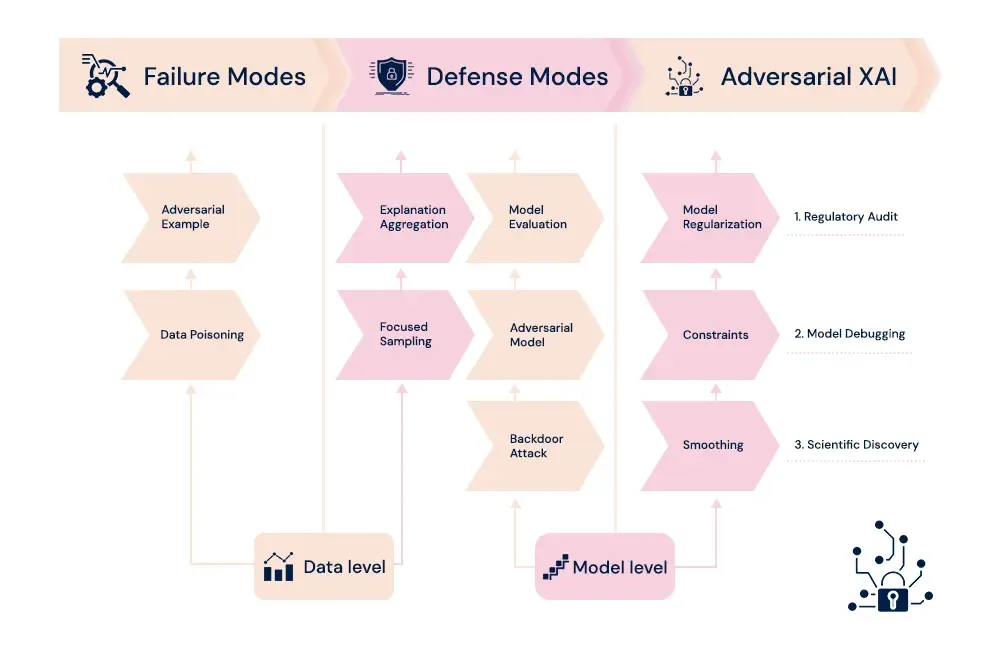
Adversarial attacks are a way to manipulate AI models with small changes in the input data so that the AI makes bad predictions or bad decisions. It is easy to imagine how dangerous this could be in the case of such consequences as health diagnostics or autonomous driving.
AI models are great intellectual properties. Model theft refers to the act of duplicating or stealing these models, which may result in financial losses and denial of competitive advantage.
Adversarial Attacks:
Adversarial attacks manipulate the AI models with slight changes in the input data, causing mispredictions or wrong decisions to be made by the AI. One can easily imagine how dangerous these could be when such applications are used in healthcare diagnosis or autonomous driving.
Model Theft and Intellectual Property (IP) Theft:
AI models are large pieces of intellectual property. Model theft involves copying or stealing these models, which may lead to financial loss and competitive disadvantage.
Bias and Fairness:
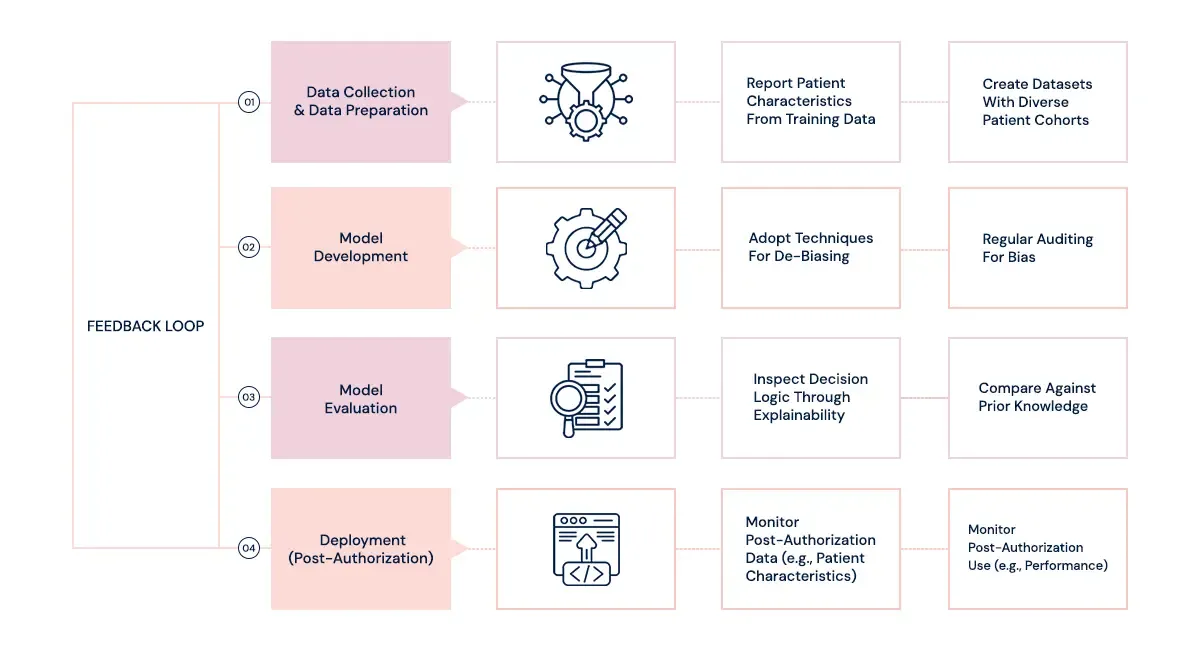
The unseen methods of AI systems can mirror such biases in the training data, leading to biased or unfair decisions. Bringing such biases to light is therefore important for the ethical deployment of AI technologies.
Risks of AI Autonomous Systems
Autonomous Systems:
Autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars, rely heavily on AI. Any security vulnerabilities within these systems may thus lead to inadvertent and catastrophic failures that could cost lives and infrastructure.
Cybersecurity Threats:
AI is both a tool and a target of cyberattacks. AI could be misused in order to enhance attack strategies, while on the other hand, AI systems can be attacked themselves, which affects their functionality.
Economic and social effects:
Huge economic and social effects arise when bad actors misapply AI. For instance, AI-driven information warfare distorts public opinion and destabilizes societies.
Reducing the Risks of Security in AI
Robust Data Handling Practices:
Information handling and storage policies should be designed to protect sensitive information. This should be supplemented with some security measures, which may include encryption, anonymization, and access controls.
Model Robustness and Testing:
Developing robust models that will ensure confidential and secure AI models that are resistant to various adversarial attacks is of prime importance. Regular testing and model updating will definitely help in trying to find the vulnerabilities and reduce them.
Ethical AI Development:
Ensuring that the processes of developing AI have intended fairness and bias mitigation is critical. Diverse datasets and practices of inclusive design may go a long way in ensuring the creation of equitable AI.
Regulation and Compliance:
The safe deployment of AI technologies may be facilitated by having them work within regulatory frameworks alongside industry standards. Organizations should stay updated on the relevant regulations and strive for compliance.
New Advanced Security Technologies:
Zero Trust Architecture:
A zero-trust architecture assumes that threats can come from both outside and inside the network. ZTA enforces strict authentication for every person and device that accesses resources; this makes AI systems much safer.
Secure Software Development Lifecycle:
Integrating security at every stage of the software development lifecycle ensures that AI systems are designed with security in mind. This includes conducting security assessments and code reviews to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities early in the development process.
Threat Intelligence and Monitoring:
Threat intelligence platforms have the ability to monitor and analyze potential threats to understand emerging risks. Continuous monitoring helps in the early detection of anomalies and enables early mitigation and response to potential security incidents.
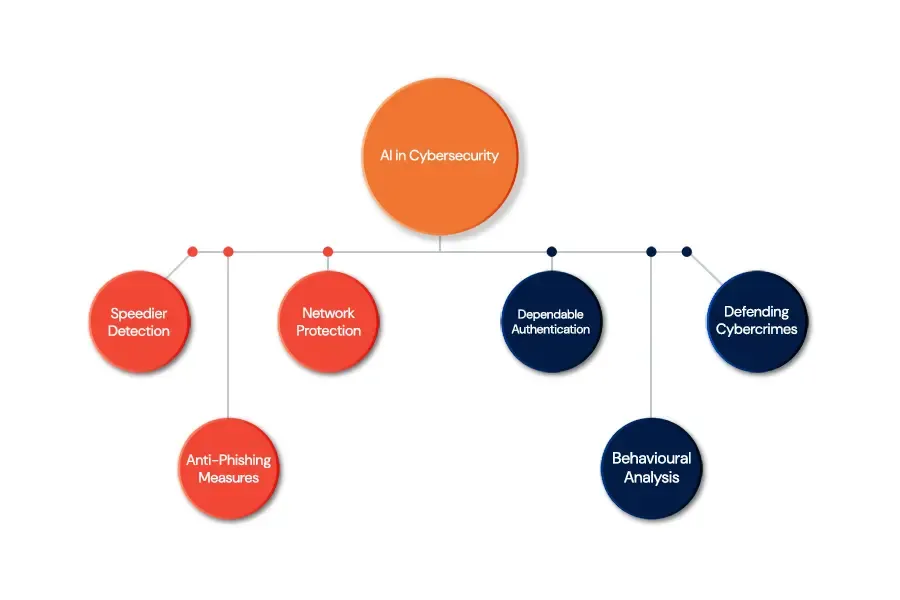
AI in Threat Detection and Response:
Using artificial intelligence to improve traditional cybersecurity measures can be very successful. AI-driven threat detection systems help identify patterns and anomalies that typically occur in the event of a cyber attack, leading to faster and more accurate responses.
Autonomous Vehicle:
Autonomous vehicles use artificial intelligence for monitoring and assistance. They must therefore maintain the safety of the systems to prevent eventualities that could clearly lead to fatal accidents. The case involving Uber's self-driving vehicle clearly shows the critical need for safety measures.
See Also: Impact of AI and ML on the Future of E-commerce
Here are a Few Case Studies:
Security in Healthcare AI:
Diagnostics has also been integrated into AI for patient care in health care. There is a call to protection in terms of ensuring that the patient's data are secure and that the administration of correct diagnostics is maintained. A noteworthy example is found in radiology, where the prevention of hacking leading to image modification for particular diagnoses will have to be considered.
Autonomous Vehicle:
Autonomous vehicles use AI for navigation and decision-making. It, therefore, has to ensure the systems' security to avoid possibilities that could lead to fatal accidents. The incident with the Uber autonomous vehicle spells out loud the necessity for robust security measures.
Conclusion
The security landscape of AI is indeed complex and constantly evolving. As AI technologies advance, addressing the associated challenges becomes increasingly crucial. Implementing safe and robust measures in an AI-powered world is essential, but this can only be effective if there is a genuine understanding of the risks involved.
Aspire Softserv is well-equipped to help navigate these challenges with our comprehensive AI development services, ensuring that your solutions are not only innovative but also secure and resilient.
Empower Your Business with Secure AI Solutions!